Tekes-funded DESME project examined how household energy behavior can be influenced by means of design.
Energy User Groups
The study found five energy user types, which differ from each other in attitudes towards saving energy s well as in the true energy saving behavior and the factors motivating energy saving. On the basis of behavior, attitudes and motives the consumers were given names: Passionate environmentalist, Active Energy Saver, Uncertain energy user, Indifferent energy user and the Reluctant energy-saver. The communications and the different energy-saving tools should be better targeted to the needs of different consumers.
Product concepts for saving energy
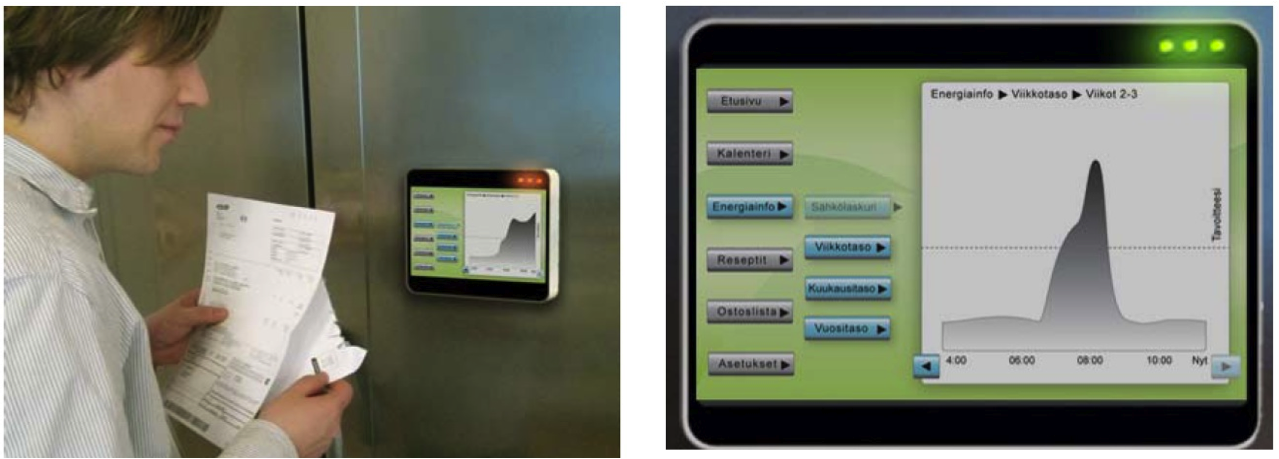
DESME project developed four energy-saving product concepts: the Energy Display adds consumer perception of their energy consumption offering easily understandable consumer information, Shower Duck notes the overwhelming use of shower water, Smart key holder turns off the house of unnecessary electrical devices when leaving home and the Energyplant offers consumption information without numbers.
The project concepts developed in the study operate as discussion openers and as indicators on how different tools for household energy saving can be created with the help of design. As energy consumers are different, this also requires a sufficient variety of products and services so that everyone can find the most suitable option for their daily lives.
Our Partners
Finnish consumers' attitudes towards energy conservation were studied in the DESME project, carried out by the Western Finland Design Centre MUOVA (University of Art and Design Helsinki / Vaasa), VaasaEMG (University of Vaasa) and the Swedish Interactive Institute. Business Partners were the Bord Gáis, Cap Gemini, Helsinki Energy, Semio, Tampere electricity network, Vaasa Electric and Telia Sonera.
